| The Genetic Code - 17 short files Mathematical patterns in assignment of codons to amino acids |
|---|
|
Astronomy
- links:
|
Elements - links:
|
The Genetic Code -
links:
|
Language - links
|
|
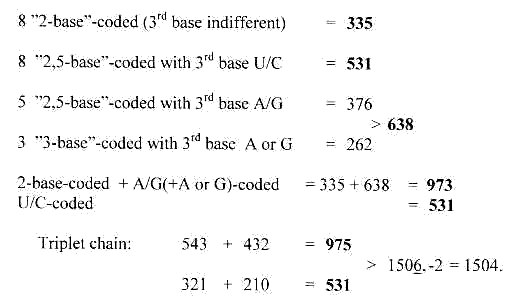
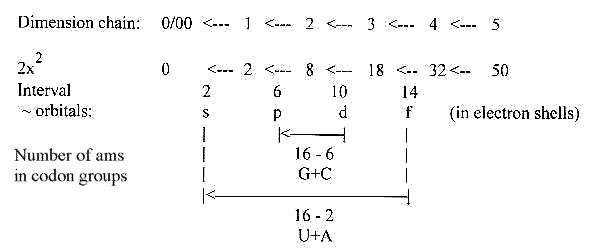
14. 3rd base grouping of codons
|
|
|
|
© Åsa Wohlin:
Free to distribute if the source is mentioned.
Texts are mostly extractions from a booklet series, made publicly available
in year 2000.
Links and Notes
Abbreviations
- ways of writing -
The
17 files
as one document, pdf
Contact:
u5d
Latest updated
2022-09-29