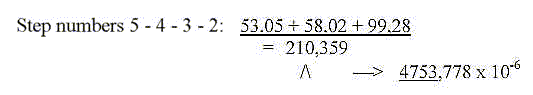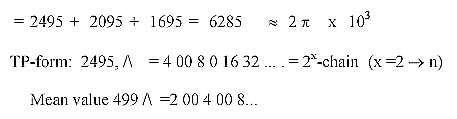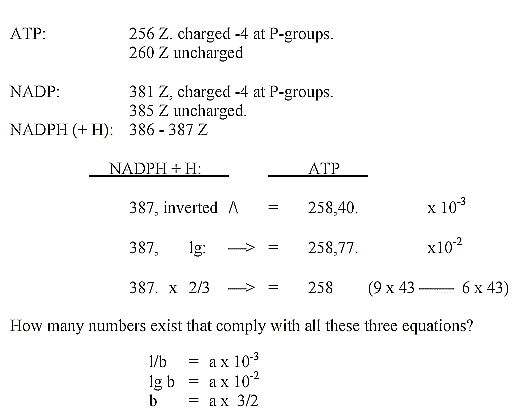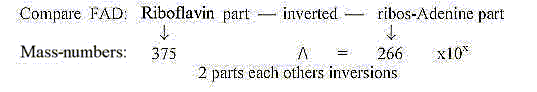|
Some elementary views:
1. How regard protein enzymes in relation to the dimension model?
They are obviously acting as "forces", binding and
breaking (~ polarizing) in relation to substrata, however, per definition,
not transforming into other molecules, not involved in that sense.
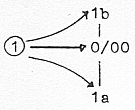
Hence, the 0- and 00-poles defining Direction as d-degree 4, a
vector geometry, which according to hypotheses in physics have been
assumed transforming (possibly through inversions) to mass and particle
structures (fermiones), is not the case here.
Instead we have to regard enzymes as expressions for these poles
when they meet in last step 1 → 0/00
of motions, the enzymes here as "oscillating" between
binding and breaking, expressions for poles 1a ("motions towards
each other", defining a new centre) and 1b ("motions from
each other", defining a new anticentre).
 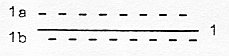 
Chains of enzymes illustrate metabolic pathways
(as such primitively seen as "linear"). There is however
only one enzyme for each step on the way. Individual enzymes represent
only the very jumps between stages (the metabolites): happenings
in their active centra with just a few amino acids involved.
One example: the enzyme which breaks fructose
dividing it in two parts, where His and Cys co-operate.
Last step 1→ 0/00 is represented
in every step of decreasing d-degree in the dimension chain (or
inwards increasing (1←0/00).
Hence, it would be possible to imagine that protein
enzymes (Ep) originated from development of secondary dimension
chains in each step of underlying chains, as the level development
have been assumed in this model. In similarity with how new bubbles
of economic activity and money circulation are developed through
history and modern societies from more direct ways of "metabolism".
An immediate objection against these sketched views
is of course that steps between metabolites or substratum/product(s)
seldom appear as changes in d-degrees in any identifiable way. Why
should they? The assumption here is that the enormous complexity
in a cell and hierarchies of newer and newer levels out of earlier
steps hide the origin in elementary dimension chains. Levels and
distribution of charge and of energy may at higher levels be the
only observable expressions for the different d-degrees.
2. Structure:
Keeping to the view on protein enzymes (Ep) as representing new
levels developed out of d-degree steps, it could explain why enzymes
geometrically enclose substrata as anti-centra in relation to centra.
In the same snse that lower d-degrees represent manifolds and anticentra
(00) in relation to higher d-degrees, superposed levels become anticentra
in relation to an underlying level.
Geometrically the relation is a typically complementary one, earlier
called "the lock and key" model, later modified
to "the induced fit model". It's a matrix relation
and one expression for the complementarity between poles in the
dimension model here.
Cavities in enzymes with hundreds of amino acids
are to a certain degree adapting to the small molecules of substrata,
which also may undergo slightly changes in structure to fit in.
This main centre of the reaction could be described
as positive/negative forms, similar to the opposition Mass/Space;
In terms of energy, this relation could be described as partly
inversed:
If the needed activating energy for a reaction
without enzymes is regarded as an energy wall, similar to the potential
wall (+) around an atomic nucleus, the complementary principle would
appear in negative energy (-) of space, as a hole.
The observations concerning activation energy levels (just decreased
by enzymes) and speed of reactions should perhaps be regarded as
only secondary results of the decisive complementarities in geometrical
forms, in charge and hydrophobic / hydrophilic polarities.
Both the long chains of amino acids in the proteins, the "global
structure"or complicated (stepwise) folding where each part
has a special function - and the specificity of the enzymes, generally
catalysing only one special reaction in their active centra, seems
to agree with the view on enzymes as developed from the steps in
the dimension chain.
Protein enzymes (Ep) with coenzymes (CoEp), including "prosthetic
groups", appear as a new level with the same anticentre - centre
relation as protein enzymes to substrata.
On this level the coenzymes as a kind of "substrata"
are carrying mass, very small molecules beginning with H+
and e- as primary "carriers of forces" on the
biochemical level. (About the coenzymes, see below.)
The coenzymes are mostly more or less closed ring-formed molecules
and many are derived from the codon bases, the nucleic acids. If
we regard the ring-forms from the aspect of sp(d)x-hybridizations,
they imply steps in the 2x2-chain
for electron orbitals
from the "end" towards
the middle of the number chain. We find similarities between
the
d-orbital shape
in some illustrations and the ac/c-relation of proteins
to coenzymes, which also include several metals in the d-orbital
of the periodic system.
We get enzymes illustrating anticentra
on different levels and in relation to different dimension steps.
RNA has also been found to have a certain catalytic capability,
and a central enzymatic function is performed by the ribosomes at
the protein synthesis (step
3 - 2 in our earlier interpretation). The
complementary polarity between the base pairs in the relation codons
— anticodons at sites of ribosomes
could perhaps be regarded as the first example of an enzymatic principle,
generalized into all enzymatic activities by pure proteins?
In that context one could ask if there is a deeper
connection between the
few amino acids chosen as active centra of Ep and the substratum,
e.g. between His and Cys and fructose? Or if they just happen to
fit the needed operation?
Mass numbers of side
chains of His and Cys is 81 and 47 (uncharged). These numbers
reappear in the distribution
of 128 C-atoms to codon grouped amino acids as well
as approximately between C-atoms of side chains
and backbone parts of 20 + 4 double-coded ams (82 - 48). First
two bases in their codons are anti-codons to each other when
read in opposite directions. Could this have a deeper sense,
a connection with the division of fructose in 2 C3-molecules
in step 3 - 2 ?
With such facts and others it seems as the
whole processes of glycolysis and citrate cycle should be regarded
as in some way "created" by the proteins,
developed from peptide relations or follow from analogous, connected
schemes, not only the other way around. (Cf. e.g. that the sum
of the 10 stations in citrate cycle + 8H from it amounts to
the same sum as the side chains of the 20 + 4 double-coded amino
acids.)
It's said that there are about 4000 catalytic reactions in a cell.
It would be interesting to know how many of these that are performed
by pure Ep-enzymes, how many through coenzymes. (An eventual number
relation?) Another question concerns the relation between structure
proteins and protein enzymes, if a border is possible to draw. The
"walking" of molecules on microtubules in cilia for instance
(and in ion canals?) have also been described as enzymatic. Correct?
If so, we have an illustration
of the last step in our dimension model from linear
d-degree 1 to motions to and from as steps in walking.
Polarities reflecting complementary features between poles
in the dimension model, a summary:
a. Protein part of enzymes versus coenzymes
b. Enzymes in relation to Substrata
c. Binding versus breaking enzymes
d. Activating versus blocking function (stimulating - inhibiting)
in regulating systems
3. Origin of protein enzymes?
It would be much easier to believe that substrata or substrata
relations create their own enzymes or in any case decide the folding
of these long protein chains, than that they are synthesized independently
and just happen to fit a certain catalysis. The "induced"
adaptation possibility of the folding of enzymes seems to reflect
a little of such a thought.
However, it should demand that proteins or chains
of amino acids in some way could create their own codons for storage
in DNA. Is there anything pointing to such a possibility in the
earlier evolution. If possible, it seems left to the future to detect.
(?)
More points to a similar but parallel evolution
of amino acids and nucleic acids, following from related schemes.
(Cf. in documents
about the genetic code mass sums of amino
acids, 2 x 544 + 2 x 208, derived from the "exponent series",
and mass of codon bases in the same chain when transformed to
number-base 8.)
We may remind of the arithmetical relations between sums of amino
acids and bases in the
figure here and ask if a similar relation could exist between
more or less virtual chains of substrata or metabolites as pathways
and the protein enzymes catalysing the steps?
(In a complex enzyme as amino acyl tRNA synthetase,
binding both tRNA, ATP(AMP) and the single, specific amino acid
for this tRNA, it has been shown that also all kind of organic bonds
are included. Bonds
that are possible to interpret as steps in a dimension chain. )
The figure referred to above with arrow bows for multiplication
could lead to another speculation:
Frameshifts in decoding of a ring-formed
RNA should lead to totally different proteins. Could such frameshifts
be connected with the difference between protein enzymes and other
structure building proteins?
Frameshifts may illustrate the brick wall principle,
however not applicable to the relations between enzymes (Ep) and
substrata, only to hierarchies of proteins.
One more question concerns the number of enzymes involved
in the transformation of a molecule as substratum to the "end"
product; for instance 5 enzymes for transformation of the amino
acid Thr to Ileu, 10 for synthesis of the amino acid His, 8 for
synthesis of Arg, according to a forgotten source.
Could these numbers of enzymes in their turn have
a deeper connection with d-degrees?
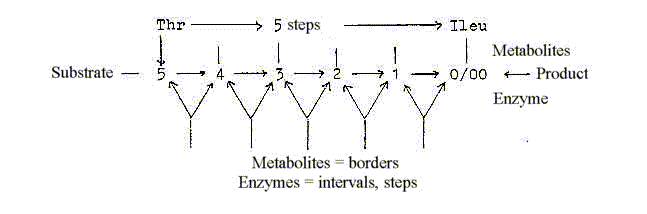
One example of enzymes transforming the amino acid
Thr to Ileu in 5 steps *:
Intervals as expressions for underlying or superposed
level - or secondary developed dimension chains in the steps? Representing
other coordinate axes?
The process here in mass numbers: -2, +44, -32
as -16, -16, + 2.
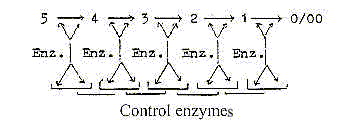
4. Control enzymes:
They illustrate the hierarchy of proteins (as of genes) and
represent still another level, a bureaucratization.
The brick wall principle, following from displacements
in half steps between levels appears as the most natural for this
relation between enzymes and control enzymes. (Possible to identify
as such?) If they control not only individual steps but the order
of steps, they represent changes of second order and may be interpreted
as substantiations of the very process as such.
In the dimension model what is motion in one d-degree
derives from a d-degree step and is structure in higher d-degrees.
A process as a series of changes may be regarded as a chain of motions.
The dimension chain of motions in the model here get the opposite
direction to the chain of structure. The motional patterns, the
changes themselves, may be substantiated during evolution, saturated
to structures.
5. Activating enzymes and product inhibition of two types:
Inhibitors as products, or substances often similar in structure,
act as a feed back mechanism. In the dimension model poles
of each d-degree have character inherited from the 0- and 00-pole
respectively as 4a ~ inward direction, 4b ~ outward direction.
Hence, the "product inhibition"
could represent this inward pole in each step, affecting the active
site of the enzyme. The complementary pole with feature from the
0-pole should represent the "feed forward" mechanism.
At the other kind of inhibition, the "allosteric"
one, an enzyme in the start of the chain is affected
and at another location than in the active site of this. It means
that the enzymes also have the centre - anticenter polarity in themselves,
centres as active sites, the anticentre expressed in the distant
other location. With the suggested illustration below it could express
a) the close connection between step 5 - 4 and 1 - 0/00 in the loop
model of a dimension chain (the polarization steps 5 →
4/1 → 3/2), and b) the connection
between anti-center at end of the chain (in d-degree 0/00 of Motions*)
with the pole 00 of d-degree 4 (00 — 4 — 0).
* (The "d-degree 0/00" substantiated
during evolution toward higher levels.)
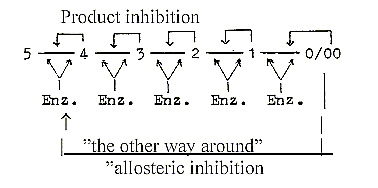
Regulating mechanisms of the types "product
inhibition" and "allosteric" inhibition":
It seems as a congruent, similar pattern of inhibition
is repeated on the higher electromagnetic level, in a developed
nervous system where a cell nearby may inhibit a cell from activation
through signals "- ½". Another system is the "lateral
inhibition" which blocks incoming signals further away from
the cell?
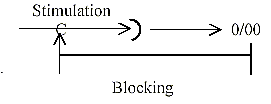
A blocking synapse on another location than in the
pathway of the signal.
A corresponding regulating structure seems to appear
between genes in DNA:
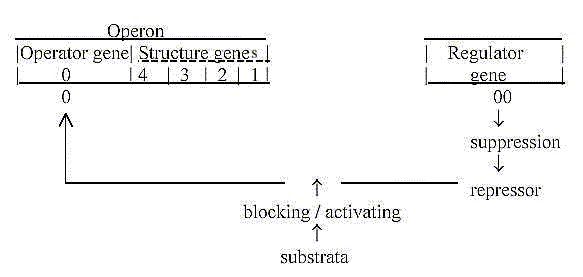
Operator gene and Regulator gene as a primary polarization
in complementary poles:
With the aspect from the dimension model in mind:
- From 0-pole: quantified steps, structure building
from inside outwards.
Structure genes connected with the 0-pole. (Cf. "feed forward"
mechanism ~ outward direction.)
- From 00-pole, the pole representing continuum,
repetition and multitude:
00 = anticentre, regulating gene in another location in the chromosome,
reminding of the "allosteric inhibition" among enzymes.
(Cf. feed back" mechanisms ~ inward direction.)
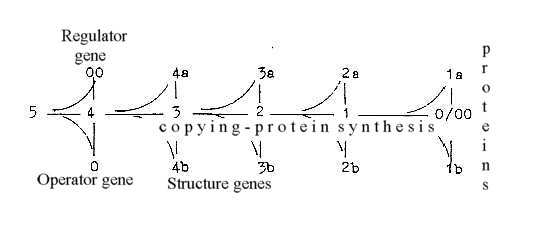
Coenzymes
Forms of the coenzymes?
An attempt to range the forms in a scheme of polarizing
steps and in a certain degree according to heaviness is made below:
Only giving a hint of eventually possible aspects.
Since most data indicate that nucleic acids and
amino acids is coupled with d-degree step 4-3 as the step for "A-Z-numbers"
of N, nitrogen, this position is kept in the sketch.
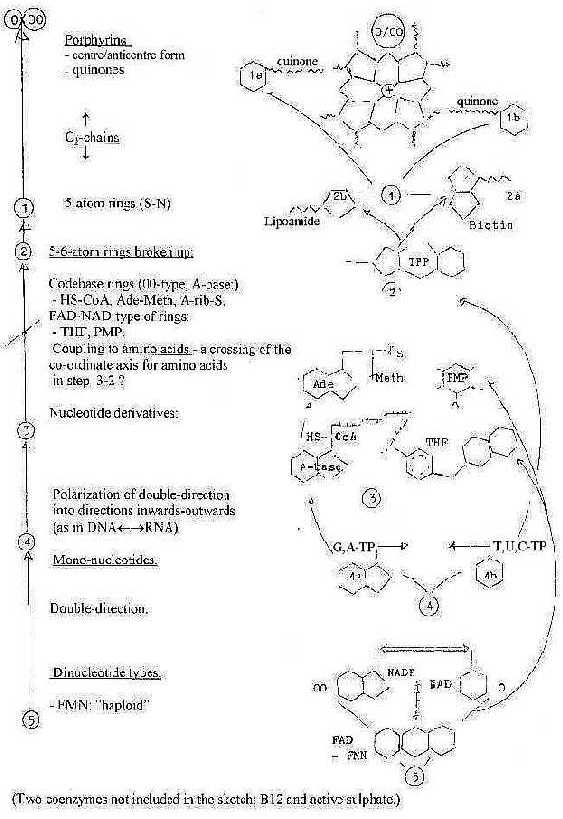
Calculations with mass numbers:
In the primary reference here (P. Karlson:Biokemi
1976) 25 coenzymes are mentioned, that's 52.
The simple number 25 became a temptation
to study the coenzymes a bit closer to see if they in some sense
could be interpreted as representing a dimension chain in agreement
with this model. Such a task is of course a very suspicious one:
Firstly, the number of coenzymes may be just a selection
out of many more. Secondly, regarding mass analysis, many of the
coenzymes appear in different forms, for instance with or without
carried groups or in -TP-, -DP-, -MP-forms etc. Following choices
were made in the table below.
- Codon base enzymes in their -TP-form.
- THF, tetrahydrofolacin as formyl-THF
- PMP, pyridoxaminphosphate (PLP-form = -1 A)
- TPP, thiaminpyrophosphate
- Ubiquinone (said to include "6-10" isoprene molecules),
here 8 supposed.
In mass numbers +1 are included for all negative charges and for
bonds to other molecules, without regard to some (balancing?) positive
charges.
5 H+ 2865
5 e- 3272
5 codon bases 2495
3+2 C1+C2 2310
3 other groups 2334
2 quinones 1478.....
Sum 14754,
-1
if PLP = 14753.
An alternative form of the dimension chain has been tested before
(not published) in connection with amino acids. Here d-degree 0/00
as equivalent with 5' is the start, hence with outer poles 1a —1b.
The superposed chain gets altered to the number chain
1-4-7-5-3:
- Triplet 975 from ordinary superposed chain (9-7-5-3-1): 97,52
= 2 x 4753,1 25.
- 2 x 753 = 1475 + 31 = 1506 = 24 amino acids (R-chains) with +2H.
(31 = Serin)
(1475 + 4753 = 3278 = 24 amino acids, R+B-chains,
with + 2H.)
- Quinones: 1-4-7-5 + 3 = 1478 A
- √543210 x 2
= 1474. = sum of quinones without 2 x 2H
- Quinones + e-group = 1478 + 3272 = 4750 A
Mean value of a coenzyme = 14753/25 = 590,12.
590 is the sum of one of the "factor chains"
The coenzymes in 5 groups - as in 5 steps - in another way, where
those transporting other molecules are split on the C2- and C1-groups.
Dividing the mass sums with factors 54, 43, 32
etc., gives a sum which is an inversion of the real total:
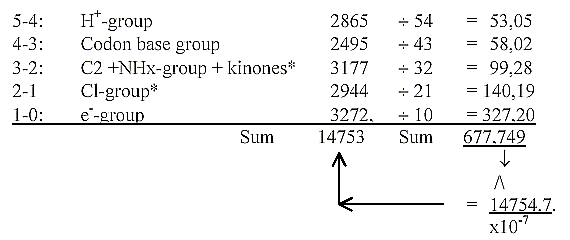 ‡ ‡
* Explanations:
3-2: C2-group HS-CoA + TPP = 1192, + Active sulphate 507 = 1699.
+ Quinones as 0/00-centres meeting in step 3-2 = 1478. Sum 3177.
2-1: C1-group 1118, + PLP + B12 = 2944.
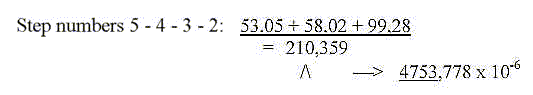
Porphyrines:
Mass sum of all 25 coenzymes with PMP: 14754.
Porphyrines, the e--transporting coenzymes: 5 cytochrome
and chlorophylls = 3272,
+ B12 (1579) = 4851. 4851 = 21 x 231 or 11 x 21 squared..
Without +1 for bonds and negative charges in cytochromes
and chlorophylls (=-6) the sum becomes 4845.
Without adding +1 for negative charges in the rest of coenzymes
and only 2 H rolled in quinones and H+-group (= -12 H) we get the
sum 9876 for the rest.
A dimension chain with poles:
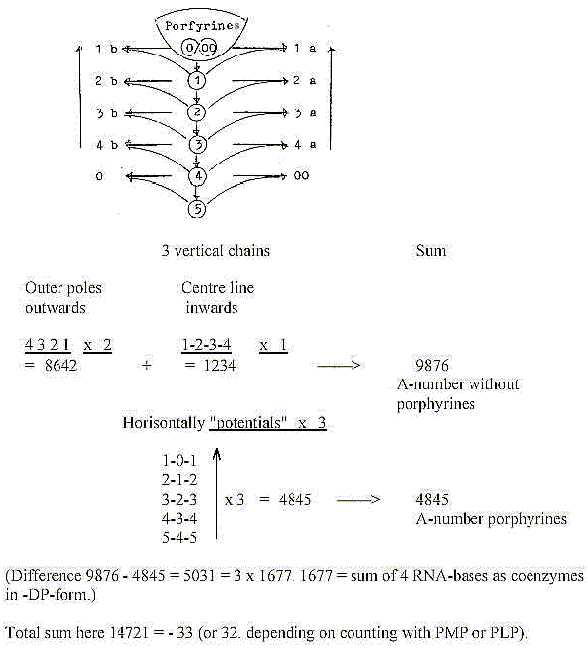
Divisions within the porphyrine group:
- The potentials of the dimension chain x 3:
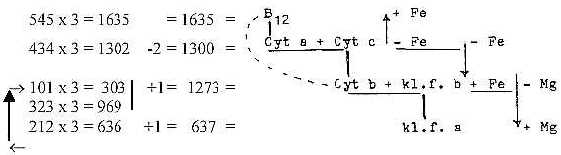
(Here porphyrines as charged and in bonds, a part
only from uncharged P-group in B12. B12 connected with activity
of haemoglobin?)
Last potential 101 should here be imagined as appearing within
the 3-2-step. There we get the border then between cytochromes and
chlorophylls, a border between plant and animal life too.
If the thought above should have some sense, it could throw light
upon why porphyrines are stored as piles (or columns), discs upon
one another just inside cell membranes, d-degree 2 in form. (Cf.
total number 4851 = number 21 for step 2-1 squared, x 11.)
And why the "virtual" displacements of the metal atoms
(here illustrated as polarized in directions on level 4-3-4; poles
4a-4b representing opposite directions)? Illustrating some transition
functions in a development towards higher d-degrees??
Sum of 5 code base enzymes in -TP-, -DP, -MP-form, uncharged:
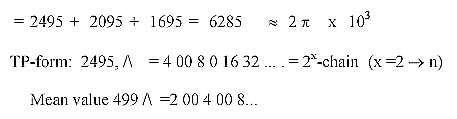
(See further about these coenzymes here,
part 2, Transformations between number-base systems.)
NADP - ATP, Z-numbers 256-260,
381-387:
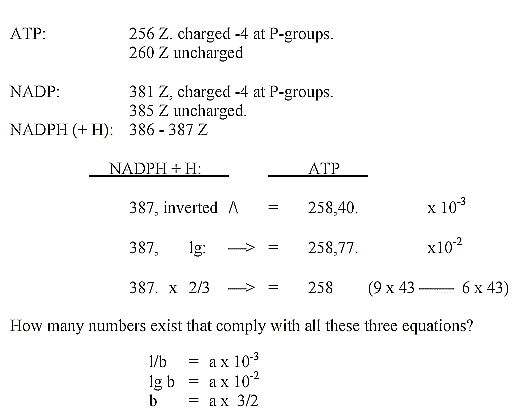
If these arithmetical relations should have some hidden
sense, it could imply that there existed some "dynamic balance"
between charges of these molecules.
Or some principle between different parts of the
molecules at the construction?

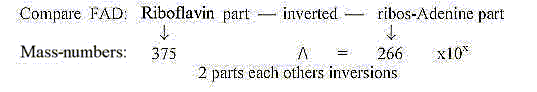
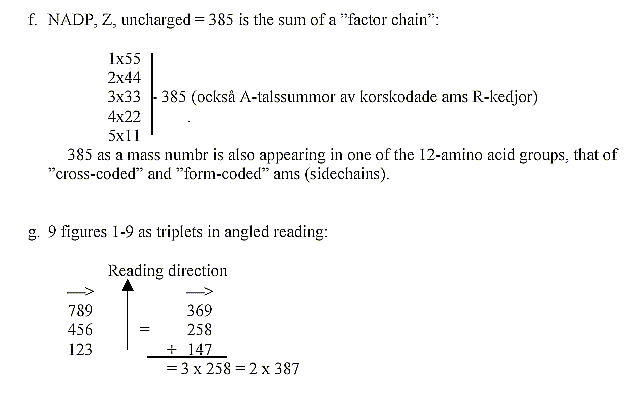
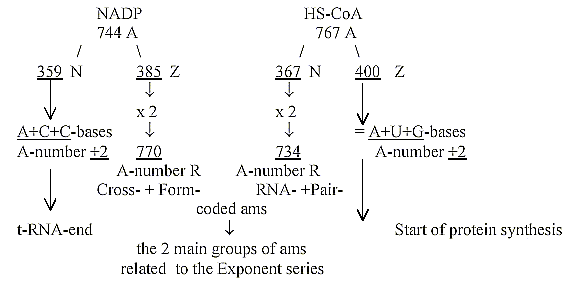
(Both these coenzymes are involved in the glycolysis
and citrate cycle, where amino acids have their origins - but these
divisions in N-Z-numbers and mixed sums seem as a cruel violation
of even the slightest possibility of a scientific theory?)
*
|












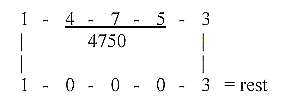
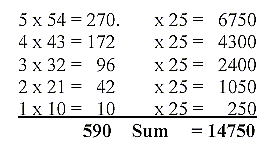
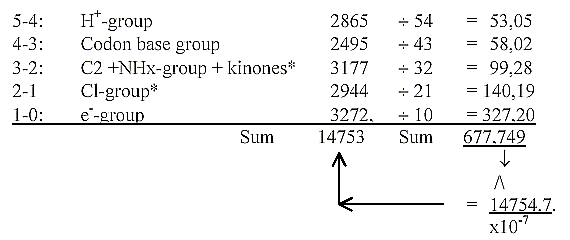 ‡
‡