|
|
|---|
|
Astronomy
- links:
|
Elements - links:
|
The Genetic Code -
links:
|
Language - links
|
|
22. Other substances Fats — Sugar — Na-Cl, Na-K-pump |
Some annotations about other substances: Fig. 22-1: Two comon fatty acids
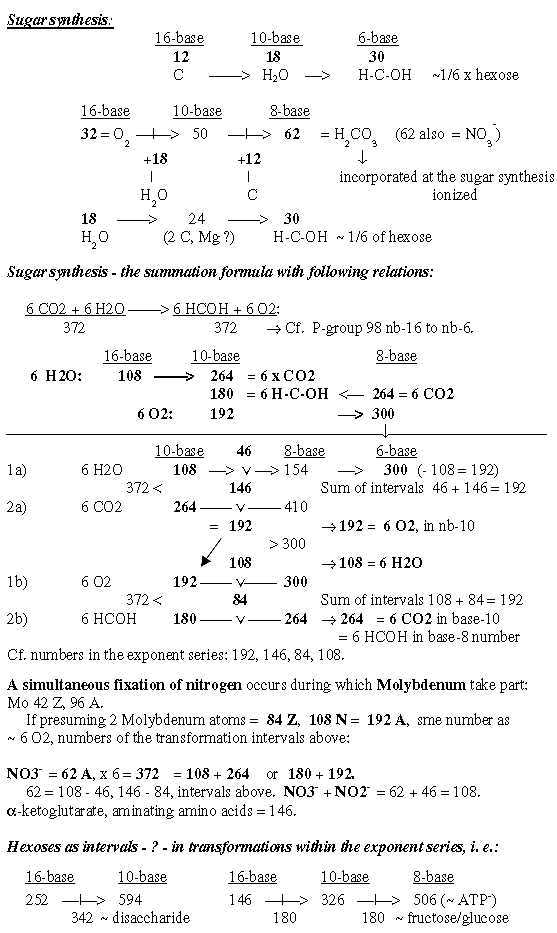
2. Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates, some examples, transformations nb-16 → 10 → 8 or → 6: - A disaccharide 342 or two hexoses 180 from ES-numbers as intervals in transformation steps:
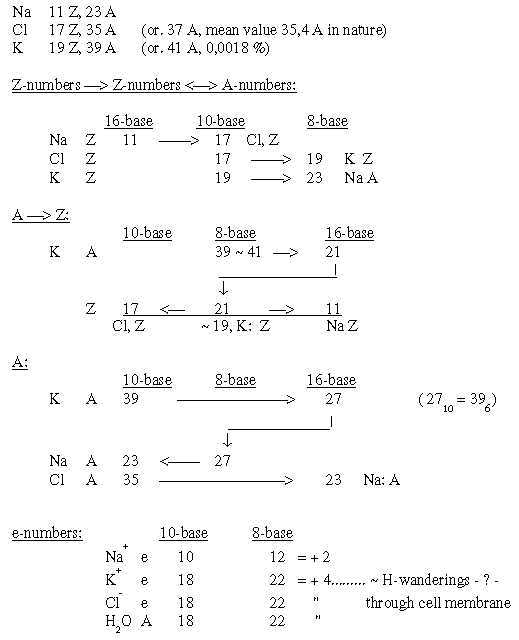
3. Na-Cl and the Na-K-pump: Na-Cl and Na-K-pump in the nervous system: Fig. 22-3: * To Discussion. |
|
|
© Åsa Wohlin
Individual research
E-mail: a.wohlin@u5d.net
Table
24 amino acids (ams)
R-chains, A, Z, N
Abbreviations
- ways of writing -
Background
model
Files here:
All
these files gathered
in one document, word,
124 p.
All these files in 3 documents, pdf:
Section
I, files 0-11
Section
II, files 12-16
Section
III, files 17-22
Discusssion, References in section III
To
17 short files.
- partly other material
-
The
17 files as one document,
pdf
An
earlier version (2007)
with more material
on the same subject, 73 pages:
Contact:
u5d
Latest updated:
2022-11-12